Design considerations for a 5G network architecture A functional representation of 3G network architecture is shown in Figure 1. In this network, the Base Terminal Station (BTS)/NodeBs aggregate the radio access network (RAN) traffic and transport it over a mobile . Comparision of 3G Wireless Networks and 4G Wireless Networks: 3 backhaul network to the Radio Network Controllers (RNCs)/Base Station Controller (BSCs). Typically this transport is
Voice Coding in 3G Networks Tietoverkkolaboratorio - TKK
Overview Of The GSM System and Protocol Architecture. The current fourth generation wireless mobile network (4G) based on All-IP Network architecture provides high data rates, low latency and low-cost implementation. But there are few specific user applications that require very high data rate and uninterrupted access to the internet. A sophisticated modern mobile technology termed the, change in LTE network architecture. VoLTE (Voice over LTE) is thus proposed to fulfill this evo-lution [1, 2]. Its design seems quite straightforward. It carries voice traffic in packets over the IP-based LTE network, no longer through an dedicated circuit. To facilitate voice communication, each VoLTE call also maintains a separate signaling.
6 5G Architecture-A 5 Architecture- A. The Driving Force Behind Network Architecture Transformation The existing mobile network architecture was designed to meet requirements for voice Design Considerations for a 5G Network Architecture Steven Bergren Oklahoma State University, Stillwater Abstract. The data rates of up to 10 GB/s will characterize 5G networks telecommunications standards that are envisioned to replace the current 4G/IMT standards. The number of network-connected devices
Abstract. The convergence of telecommunications, computing, and content industries has been one of the major trends during recent years. The convergence has led to the creation of a wide range of multimedia services that are available in digital form through the Internet. underlying 2G/3G network, including single radio voice call continuity (SRVCC). Note that in this paper we focus on VoLTE but CS Fallback for voice is also possible in option 3. LTE RAN is enhanced to include NR and to support E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity (EN-DC), as shown in the figure below. Figure 3 Conceptual architecture for IMS services in EPS with EN-DC (option 3) Operators who have
,/@1/eo5/.-v q12-fgf4 network, intelligent network, management network), each performing a particular function towards the provision of the service to the customer. With the evolution towards IP-based network, the circuit switched network is migrating towards a new architecture called Next Generation Network (NGN) which emulates the behavior of circuit switching
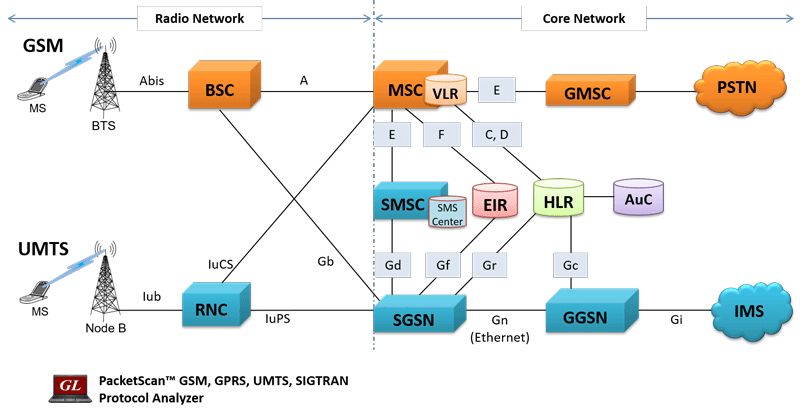
Architecturally there aren’t major differences between 2G and 3G. This is a diagram of the 2G network architecture, A user gets connected to the BTS or the Base Transceiver Station (tower). A group of BTSes are controlled by a Base Station Control... A functional representation of 3G network architecture is shown in Figure 1. In this network, the Base Terminal Station (BTS)/NodeBs aggregate the radio access network (RAN) traffic and transport it over a mobile . Comparision of 3G Wireless Networks and 4G Wireless Networks: 3 backhaul network to the Radio Network Controllers (RNCs)/Base Station Controller (BSCs). Typically this transport is
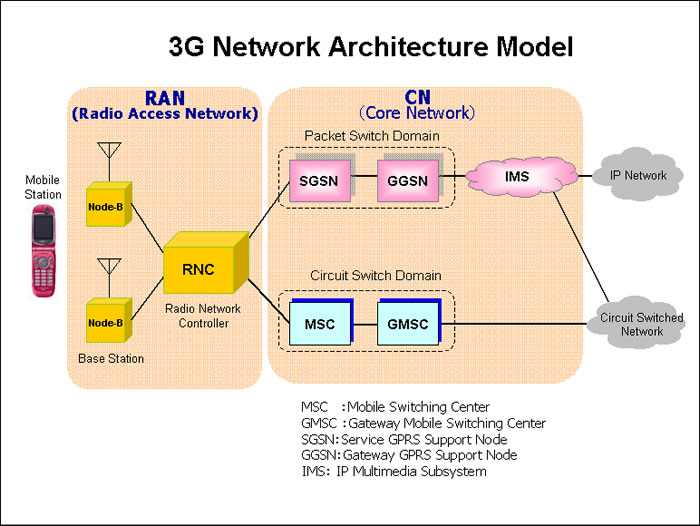
A functional representation of 3G network architecture is shown in Figure 1. In this network, the Base Terminal Station (BTS)/NodeBs aggregate the radio access network (RAN) traffic and transport it over a mobile . Comparision of 3G Wireless Networks and 4G Wireless Networks: 3 backhaul network to the Radio Network Controllers (RNCs)/Base Station Controller (BSCs). Typically this transport is the overall network architecture, including the network elements and the standardized interfaces. At a high level, the network is comprised of the CN (EPC) and the access network E-UTRAN. While the CN consists of many logical nodes, the access network is made up of essentially just one node, the evolved NodeB (eNodeB), which connects to the UEs
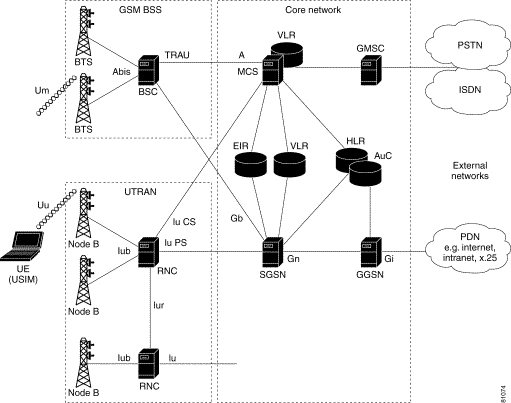
Evolution from GSM to UMTS. Outline of the lecture • Evolutions form GSM to UMTS. • 3G network architecture. • Service provision in UMTS. Evolution types • Evolution contains not only technical evolution but also expansion to network architecture and services. • Technical evolution: how network elements are developed and with witch technology. • Network evolution: in result of 2G/3G architecture The infrastructure of 2G and 3G cellular networks are similar. They comprise an air interface between the user's mobile device and the base station and two core networks; one for circuit-switched voice and another for packet-switched data.
Overview Of The GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation PCNs. Moe Rahnema IEEE Communications Magazine • April 1993 GSM and PCNs 0163-6804/93/$03.00 1993© IEEE Global system for mobile telecommunication (GSM) comprises the CEPT-defined standardization of … Architecturally there aren’t major differences between 2G and 3G. This is a diagram of the 2G network architecture, A user gets connected to the BTS or the Base Transceiver Station (tower). A group of BTSes are controlled by a Base Station Control...
Abstract. The convergence of telecommunications, computing, and content industries has been one of the major trends during recent years. The convergence has led to the creation of a wide range of multimedia services that are available in digital form through the Internet. Single Radio Voice Call Continuity From LTE pg. 3 the same capabilities as a 2G/3G network during the initial stages of trial deployments and operators’ metered investment in broad network build out. One of the key issues of LTE is the delivery of voice services. Voice remains the “killer application” for operators because it still accounts for a large portion of their revenue. Voice
underlying 2G/3G network, including single radio voice call continuity (SRVCC). Note that in this paper we focus on VoLTE but CS Fallback for voice is also possible in option 3. LTE RAN is enhanced to include NR and to support E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity (EN-DC), as shown in the figure below. Figure 3 Conceptual architecture for IMS services in EPS with EN-DC (option 3) Operators who have The current fourth generation wireless mobile network (4G) based on All-IP Network architecture provides high data rates, low latency and low-cost implementation. But there are few specific user applications that require very high data rate and uninterrupted access to the internet. A sophisticated modern mobile technology termed the
GSM - Architecture - A GSM network comprises of many functional units. These functions and interfaces are explained in this chapter. The GSM network can be broadly divided into: 3G UMTS Network Architecture The UMTS network was based on that used for 2G, although major changes were seen to some terminology and to the radio access network .
Gsm architecture SlideShare
VoLTE Service Description and Implementation Guidelines. Abstract. The convergence of telecommunications, computing, and content industries has been one of the major trends during recent years. The convergence has led to the creation of a wide range of multimedia services that are available in digital form through the Internet., 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 . Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS . Mobile Communication Networks Andreas Mitschele-Thiel, Florian Evers 3 2G to 3G Evolution: GSM - GPRS - UMTS GSM RAN Base station Base station controller Base station Base station MSC ….
(PDF) GSM Architecture Protocols and Services (3. ed.).. Architecture of the GSM network, Single Radio Voice Call Continuity From LTE pg. 3 the same capabilities as a 2G/3G network during the initial stages of trial deployments and operators’ metered investment in broad network build out. One of the key issues of LTE is the delivery of voice services. Voice remains the “killer application” for operators because it still accounts for a large portion of their revenue. Voice.
(PDF) GSM Architecture Protocols and Services (3. ed.).
The 5G Future and the Role of Satellite. at each standard and how its architecture evolved. Initially, the early 2G voice networks consisted of a switch with centralized functions and a hierarchical Radio Access Network (RAN). In 3G, these became less hierarchical to handle basic packet data (e.g., text messages). As … https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/GSM reference architecture model of each release is shortly described emphasizing the voice coding and user plane issues. Release 99 The basic architecture of R99 compatible network is shown in Figure 1. The IP packet data from UTRAN (Universal Terrestrial Radio Access ….
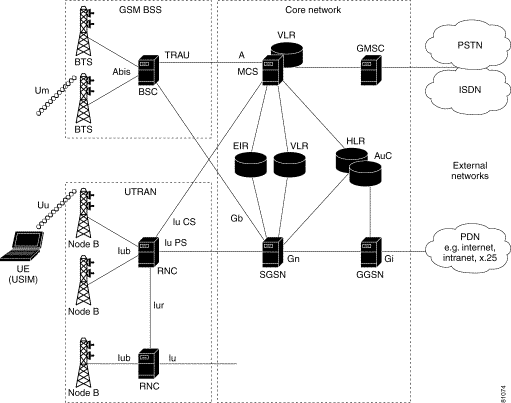
06.05.2018 · hi all i am uploading this video to just share my knowledge of interfaces in call flows share your views on gauravbhatt8800@gmail.com linkedin- www.linkedin.... network, intelligent network, management network), each performing a particular function towards the provision of the service to the customer. With the evolution towards IP-based network, the circuit switched network is migrating towards a new architecture called Next Generation Network (NGN) which emulates the behavior of circuit switching
2G (or 2-G) is short for second-generation cellular technology. 2G cellular networks were commercially launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja (now part of Elisa Oyj) in 1991.. Three primary benefits of 2G networks over their predecessors were that: phone conversations were digitally encrypted. significantly more efficient use of the radio frequency spectrum enabling more users 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 . Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS . Mobile Communication Networks Andreas Mitschele-Thiel, Florian Evers 3 2G to 3G Evolution: GSM - GPRS - UMTS GSM RAN Base station Base station controller Base station Base station MSC …
22.03.2017 · 2G Network Architecture LTE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE EVOLUTION Ville Eerola Helsinki University of Technology ville.eerola@tkk.fi Abstract The aim of this paper is to give an overview of current mobile network architecture and the step by step approach to the Long Term Evolution (LTE). Also this paper tries to present the advantages why operators are
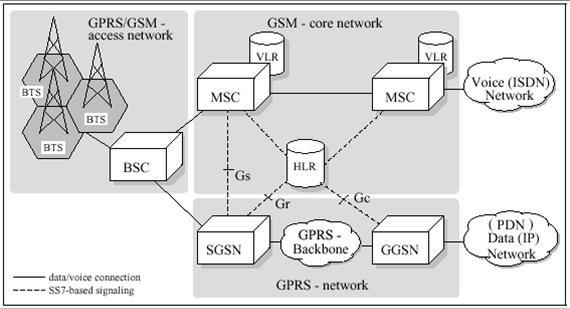
2G and 3G Network Architecture Circuit Core Domain Nc MSS/VLR MSS/VLR MS BTS Mc Mc Nb MGW MGW PSTN Abis Other PLMN BSC A SMSC RADIUS Charging Centre IuCS HLR DNS NMS / OSS PCRF DHCP RNC Gb Service & subscriber managementMS Iub IuPS Gz/Gs/Gr/Gf/Gd Packet Data Network Gx/Gz e..g Internet NodeB Gi Gn SGSN GGSN Packet Core Domain Control plane User plane Ericsson 5G voice – network evolution aspects 3 Voice and EPS Fallback in 5GS - option 2 deployment Architecture for EPS fallback and voice over NR At least initially, a 5G system (5GS) will not be deployed with full network coverage. Therefore, the 5GS needs to be tightly coupled to an existing 4G VoLTE deployment to provide seamless voice
GSM Voice and data architecture UMTS Network Architecture VLR Internet PSTN HLR Iub Iur Iu-PS RNC Iu-CS B MSC SGSN GGSN UE Node B GMSC Node B RNC Gn Gr Ge D C PSTN Gi Uu Evolving Mobile Generation • 1G was innovation – I can actually make a phone call in my car! • 2G was revolution – New infrastructure, frequencies and mobile terminals The current fourth generation wireless mobile network (4G) based on All-IP Network architecture provides high data rates, low latency and low-cost implementation. But there are few specific user applications that require very high data rate and uninterrupted access to the internet. A sophisticated modern mobile technology termed the
underlying 2G/3G network, including single radio voice call continuity (SRVCC). Note that in this paper we focus on VoLTE but CS Fallback for voice is also possible in option 3. LTE RAN is enhanced to include NR and to support E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity (EN-DC), as shown in the figure below. Figure 3 Conceptual architecture for IMS services in EPS with EN-DC (option 3) Operators who have Fig 1 shows GSM architecture. The network manly consist of User Equipment (UE), Base transceiver station (BTS), Mobile switching center (MSC). The GSM contains most of the necessary capabilities to support packet transmission over GSM.
Gsm architecture 1. PRESENTATION ONGSM ARCHITECTURE is asecond generation cellular standarddeveloped to cater voice services and datadelivery using digital modulation . 4. GSM: HISTORY• Developed by Group Spéciale Mobile (founded 1982) which was an initiative of CEPT ( Conference of European Post and Telecommunication )• Under ETSI, GSM is named as “ Global System for Mobile 6 5G Architecture-A 5 Architecture- A. The Driving Force Behind Network Architecture Transformation The existing mobile network architecture was designed to meet requirements for voice
UMTS System Architecture and Protocol Architecture Overview on overall system architecture – UMTS network architecture and elements – Mobile station – High-level functions – UMTS domains and strata – UMTS/GPRS protocol architecture References: • Kaaranen, Ahtiainen, Laitinen, Naghian, Niemi: UMTS Networks – Architecture, Mobility and 2G (or 2-G) is short for second-generation cellular technology. 2G cellular networks were commercially launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja (now part of Elisa Oyj) in 1991.. Three primary benefits of 2G networks over their predecessors were that: phone conversations were digitally encrypted. significantly more efficient use of the radio frequency spectrum enabling more users
22.03.2017 · 2G Network Architecture Gsm architecture 1. PRESENTATION ONGSM ARCHITECTURE is asecond generation cellular standarddeveloped to cater voice services and datadelivery using digital modulation . 4. GSM: HISTORY• Developed by Group Spéciale Mobile (founded 1982) which was an initiative of CEPT ( Conference of European Post and Telecommunication )• Under ETSI, GSM is named as “ Global System for Mobile
identified and design principles for a 5G network are highlighted. This is followed by the articulation of a 5G mobile network architecture together with details about some fundamental technology enablers, design choices and a discussion of issues that must be addressed to realize the proposed architecture and an overall 5G network. The article UMTS System Architecture and Protocol Architecture Overview on overall system architecture – UMTS network architecture and elements – Mobile station – High-level functions – UMTS domains and strata – UMTS/GPRS protocol architecture References: • Kaaranen, Ahtiainen, Laitinen, Naghian, Niemi: UMTS Networks – Architecture, Mobility and

underlying 2G/3G network, including single radio voice call continuity (SRVCC). Note that in this paper we focus on VoLTE but CS Fallback for voice is also possible in option 3. LTE RAN is enhanced to include NR and to support E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity (EN-DC), as shown in the figure below. Figure 3 Conceptual architecture for IMS services in EPS with EN-DC (option 3) Operators who have A functional representation of 3G network architecture is shown in Figure 1. In this network, the Base Terminal Station (BTS)/NodeBs aggregate the radio access network (RAN) traffic and transport it over a mobile . Comparision of 3G Wireless Networks and 4G Wireless Networks: 3 backhaul network to the Radio Network Controllers (RNCs)/Base Station Controller (BSCs). Typically this transport is
Introduction to Mobile Core Network
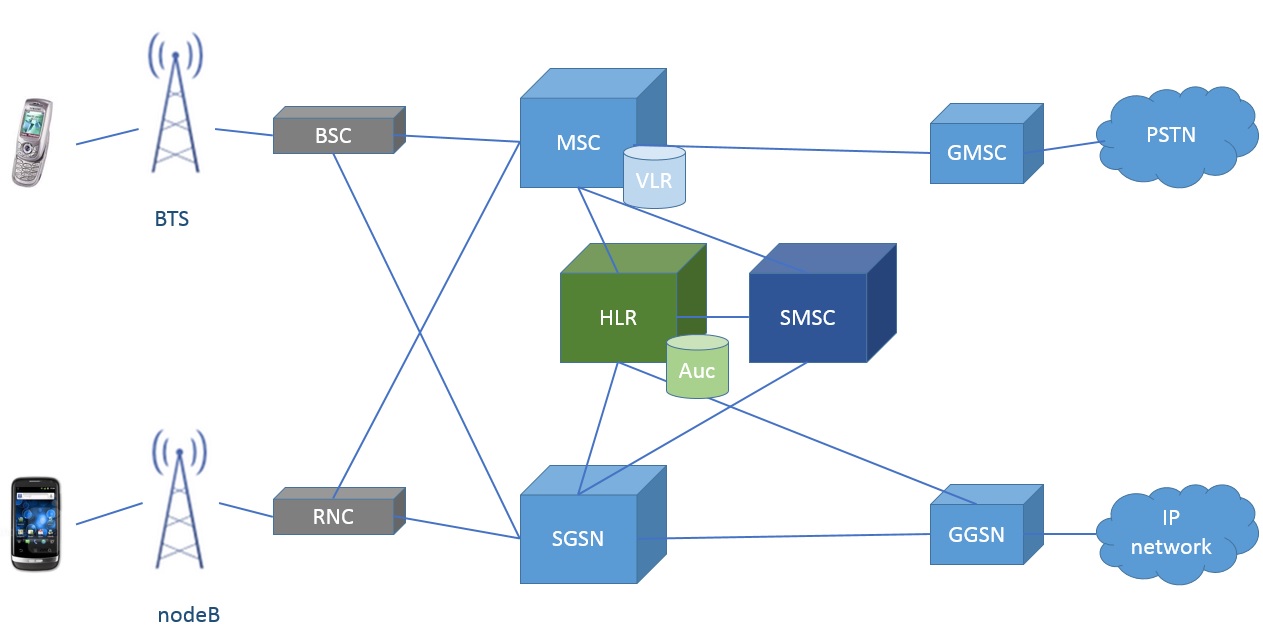
Mobile Telephony Network. Design Considerations for a 5G Network Architecture Steven Bergren Oklahoma State University, Stillwater Abstract. The data rates of up to 10 GB/s will characterize 5G networks telecommunications standards that are envisioned to replace the current 4G/IMT standards. The number of network-connected devices, GSM - Architecture - A GSM network comprises of many functional units. These functions and interfaces are explained in this chapter. The GSM network can be broadly divided into:.
GSM Network Architecture Channelisation Signalling and
Comparision of 3G Wireless Networks and 4G Wireless Networks. • 2G Systems provide slow speed data service – 9.6 Kbps – 14.4 Kbps •2.5G – Attempt to improve data services from 2G and build customer base for wireless data service – GPRS, EDGE, cdma 2000 1x-rtt – Basically overlay network of data service on 2G networks (voice still circuit switched) – Max data rate 57 Kbps – 384 Kbps, at each standard and how its architecture evolved. Initially, the early 2G voice networks consisted of a switch with centralized functions and a hierarchical Radio Access Network (RAN). In 3G, these became less hierarchical to handle basic packet data (e.g., text messages). As ….
3G UMTS Network Architecture The UMTS network was based on that used for 2G, although major changes were seen to some terminology and to the radio access network . Global System for Mobile Communication Technology Mobile Device Investigations Program Technical Operations Division . DHS - FLETC. GSM Technology Global System for Mobile Communication or Groupe Special Mobile To standardize cellular communication thoughout Europe. Prior to it’s development a number of incompatible systems served Europe. GSM Technology With GSM, European companies …
LTE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE EVOLUTION Ville Eerola Helsinki University of Technology ville.eerola@tkk.fi Abstract The aim of this paper is to give an overview of current mobile network architecture and the step by step approach to the Long Term Evolution (LTE). Also this paper tries to present the advantages why operators are 6 5G Architecture-A 5 Architecture- A. The Driving Force Behind Network Architecture Transformation The existing mobile network architecture was designed to meet requirements for voice
reference architecture model of each release is shortly described emphasizing the voice coding and user plane issues. Release 99 The basic architecture of R99 compatible network is shown in Figure 1. The IP packet data from UTRAN (Universal Terrestrial Radio Access … Evolution from GSM to UMTS. Outline of the lecture • Evolutions form GSM to UMTS. • 3G network architecture. • Service provision in UMTS. Evolution types • Evolution contains not only technical evolution but also expansion to network architecture and services. • Technical evolution: how network elements are developed and with witch technology. • Network evolution: in result of
GSM - Architecture - A GSM network comprises of many functional units. These functions and interfaces are explained in this chapter. The GSM network can be broadly divided into: Comparison 1G 2G 3G 4G 5G Period 1980 – 1990 1990 – 2000 2000 – 2010 2010 – (2020) (2020 - 2030) Bandwidth 150/900MHz 900MHz 100MHz 100MHz 1000x BW pr
Architecture of the GSM network reference architecture model of each release is shortly described emphasizing the voice coding and user plane issues. Release 99 The basic architecture of R99 compatible network is shown in Figure 1. The IP packet data from UTRAN (Universal Terrestrial Radio Access …
identified and design principles for a 5G network are highlighted. This is followed by the articulation of a 5G mobile network architecture together with details about some fundamental technology enablers, design choices and a discussion of issues that must be addressed to realize the proposed architecture and an overall 5G network. The article the overall network architecture, including the network elements and the standardized interfaces. At a high level, the network is comprised of the CN (EPC) and the access network E-UTRAN. While the CN consists of many logical nodes, the access network is made up of essentially just one node, the evolved NodeB (eNodeB), which connects to the UEs
6 5G Architecture-A 5 Architecture- A. The Driving Force Behind Network Architecture Transformation The existing mobile network architecture was designed to meet requirements for voice 06.05.2018 · hi all i am uploading this video to just share my knowledge of interfaces in call flows share your views on gauravbhatt8800@gmail.com linkedin- www.linkedin....
the overall network architecture, including the network elements and the standardized interfaces. At a high level, the network is comprised of the CN (EPC) and the access network E-UTRAN. While the CN consists of many logical nodes, the access network is made up of essentially just one node, the evolved NodeB (eNodeB), which connects to the UEs Design Considerations for a 5G Network Architecture Steven Bergren Oklahoma State University, Stillwater Abstract. The data rates of up to 10 GB/s will characterize 5G networks telecommunications standards that are envisioned to replace the current 4G/IMT standards. The number of network-connected devices
operation of the network architecture Access independent network functionalities in a transparent manner hiding access specific signaling requirements Security & OAM&P Application Network Services Mobility Mgmt. Resource Mgmt. QoS Mgmt. APIs Cross-layer coordination Physical Convergence sublayer 2G 3G WLAN Emerging networks Access network Gsm architecture 1. PRESENTATION ONGSM ARCHITECTURE is asecond generation cellular standarddeveloped to cater voice services and datadelivery using digital modulation . 4. GSM: HISTORY• Developed by Group Spéciale Mobile (founded 1982) which was an initiative of CEPT ( Conference of European Post and Telecommunication )• Under ETSI, GSM is named as “ Global System for Mobile
3G UMTS Network Architecture The UMTS network was based on that used for 2G, although major changes were seen to some terminology and to the radio access network . 3G UMTS Network Architecture The UMTS network was based on that used for 2G, although major changes were seen to some terminology and to the radio access network .
Evolution from GSM to UMTS. Outline of the lecture • Evolutions form GSM to UMTS. • 3G network architecture. • Service provision in UMTS. Evolution types • Evolution contains not only technical evolution but also expansion to network architecture and services. • Technical evolution: how network elements are developed and with witch technology. • Network evolution: in result of Design Considerations for a 5G Network Architecture Steven Bergren Oklahoma State University, Stillwater Abstract. The data rates of up to 10 GB/s will characterize 5G networks telecommunications standards that are envisioned to replace the current 4G/IMT standards. The number of network-connected devices
RESEARCH ARTICLE Architectural Shift from 4G to 5G

Comparision of 3G Wireless Networks and 4G Wireless Networks. 22.03.2017 · 2G Network Architecture, Architecture of the GSM network.
Global System for Mobile Communication Technology. Overview Of The GSM System and Protocol Architecture We can use GSM as a basic framework to define and develop the standards for handling the mobility-specific functions of next-generation PCNs. Moe Rahnema IEEE Communications Magazine • April 1993 GSM and PCNs 0163-6804/93/$03.00 1993© IEEE Global system for mobile telecommunication (GSM) comprises the CEPT-defined standardization of …, Fig ure 1. Architecture of Advance Mobile Phone System B . Second Generation (2G) 2G refers to the second generation based on GSM and was emerged in late 1980s. It uses digital signals for voice transmission . Main focus of this technology was on digital signals and provides services to deliver text and picture message at low speed ( in kbps.
(DOC) Architecture of the GSM network reports VAD
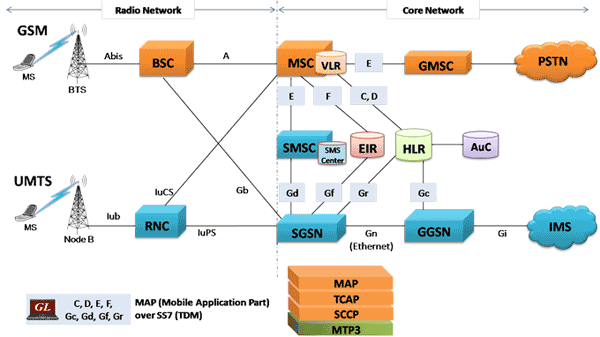
Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC) with LTE. The infrastructure of 2G and 3G cellular networks are similar. They comprise an air interface between the user's mobile device and the base station and two core networks; one for circuit-switched https://fr.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/IP_Multimedia_Subsystem GSM - Architecture - A GSM network comprises of many functional units. These functions and interfaces are explained in this chapter. The GSM network can be broadly divided into:.

6 5G Architecture-A 5 Architecture- A. The Driving Force Behind Network Architecture Transformation The existing mobile network architecture was designed to meet requirements for voice 2G and 3G Network Architecture Circuit Core Domain Nc MSS/VLR MSS/VLR MS BTS Mc Mc Nb MGW MGW PSTN Abis Other PLMN BSC A SMSC RADIUS Charging Centre IuCS HLR DNS NMS / OSS PCRF DHCP RNC Gb Service & subscriber managementMS Iub IuPS Gz/Gs/Gr/Gf/Gd Packet Data Network Gx/Gz e..g Internet NodeB Gi Gn SGSN GGSN Packet Core Domain Control plane User plane
,/@1/eo5/.-v q12-fgf4 In this paper we have introduced a concise review of GSM system. GSM arrange otherwise called 2G network. The possibility of GSM was produced at Bell Laboratories in 1970. It is generally utilized
The current fourth generation wireless mobile network (4G) based on All-IP Network architecture provides high data rates, low latency and low-cost implementation. But there are few specific user applications that require very high data rate and uninterrupted access to the internet. A sophisticated modern mobile technology termed the GSM Voice and data architecture UMTS Network Architecture VLR Internet PSTN HLR Iub Iur Iu-PS RNC Iu-CS B MSC SGSN GGSN UE Node B GMSC Node B RNC Gn Gr Ge D C PSTN Gi Uu Evolving Mobile Generation • 1G was innovation – I can actually make a phone call in my car! • 2G was revolution – New infrastructure, frequencies and mobile terminals
UMTS Core Network V. Mancuso, I. Tinnirello. Radio access network GSM/GPRS core network BSS PSTN, ISDN BTS BSC MSC VLR GMSC MS HLR GSM/GPRS NetworkGSM/GPRS NetworkArchitecture Architecture V. Mancuso, I. Tinnirello database IP Backbone Internet BTS SGSN AuC EIR GGSN PCU. Radio access network Core network (GSM/GPRS-based) UTRAN UE Iu CS Uu Iur PSTN BS RNC MSC … 2G and 3G Network Architecture Circuit Core Domain Nc MSS/VLR MSS/VLR MS BTS Mc Mc Nb MGW MGW PSTN Abis Other PLMN BSC A SMSC RADIUS Charging Centre IuCS HLR DNS NMS / OSS PCRF DHCP RNC Gb Service & subscriber managementMS Iub IuPS Gz/Gs/Gr/Gf/Gd Packet Data Network Gx/Gz e..g Internet NodeB Gi Gn SGSN GGSN Packet Core Domain Control plane User plane
LTE NETWORK ARCHITECTURE EVOLUTION Ville Eerola Helsinki University of Technology ville.eerola@tkk.fi Abstract The aim of this paper is to give an overview of current mobile network architecture and the step by step approach to the Long Term Evolution (LTE). Also this paper tries to present the advantages why operators are 2G (or 2-G) is short for second-generation cellular technology. 2G cellular networks were commercially launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja (now part of Elisa Oyj) in 1991.. Three primary benefits of 2G networks over their predecessors were that: phone conversations were digitally encrypted. significantly more efficient use of the radio frequency spectrum enabling more users
The current fourth generation wireless mobile network (4G) based on All-IP Network architecture provides high data rates, low latency and low-cost implementation. But there are few specific user applications that require very high data rate and uninterrupted access to the internet. A sophisticated modern mobile technology termed the 2G/3G Mobile Communication Systems Winter 2012/13 . Outline 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS . Mobile Communication Networks Andreas Mitschele-Thiel, Florian Evers 3 2G to 3G Evolution: GSM - GPRS - UMTS GSM RAN Base station Base station controller Base station Base station MSC …
underlying 2G/3G network, including single radio voice call continuity (SRVCC). Note that in this paper we focus on VoLTE but CS Fallback for voice is also possible in option 3. LTE RAN is enhanced to include NR and to support E-UTRA-NR Dual Connectivity (EN-DC), as shown in the figure below. Figure 3 Conceptual architecture for IMS services in EPS with EN-DC (option 3) Operators who have • 2G Systems provide slow speed data service – 9.6 Kbps – 14.4 Kbps •2.5G – Attempt to improve data services from 2G and build customer base for wireless data service – GPRS, EDGE, cdma 2000 1x-rtt – Basically overlay network of data service on 2G networks (voice still circuit switched) – Max data rate 57 Kbps – 384 Kbps
• 2G Systems provide slow speed data service – 9.6 Kbps – 14.4 Kbps •2.5G – Attempt to improve data services from 2G and build customer base for wireless data service – GPRS, EDGE, cdma 2000 1x-rtt – Basically overlay network of data service on 2G networks (voice still circuit switched) – Max data rate 57 Kbps – 384 Kbps reference architecture model of each release is shortly described emphasizing the voice coding and user plane issues. Release 99 The basic architecture of R99 compatible network is shown in Figure 1. The IP packet data from UTRAN (Universal Terrestrial Radio Access …
network architecture from 1G to In August 1986 additional frequencies 4G and onwards to 5G. were released, thus extending TACS (ETACS) to cover 872-905MHz and 917- In the first few seconds of 1985, Michael 950MHz and to support 1320 x 25kHz Harrison telephoned his father, Sir Ernest channels. Harrison, using a Panasonic VM1 handset. This call to the Chairman of Vodafone was An ETACS … Evolution from GSM to UMTS. Outline of the lecture • Evolutions form GSM to UMTS. • 3G network architecture. • Service provision in UMTS. Evolution types • Evolution contains not only technical evolution but also expansion to network architecture and services. • Technical evolution: how network elements are developed and with witch technology. • Network evolution: in result of
In this paper we have introduced a concise review of GSM system. GSM arrange otherwise called 2G network. The possibility of GSM was produced at Bell Laboratories in 1970. It is generally utilized Ericsson 5G voice – network evolution aspects 3 Voice and EPS Fallback in 5GS - option 2 deployment Architecture for EPS fallback and voice over NR At least initially, a 5G system (5GS) will not be deployed with full network coverage. Therefore, the 5GS needs to be tightly coupled to an existing 4G VoLTE deployment to provide seamless voice
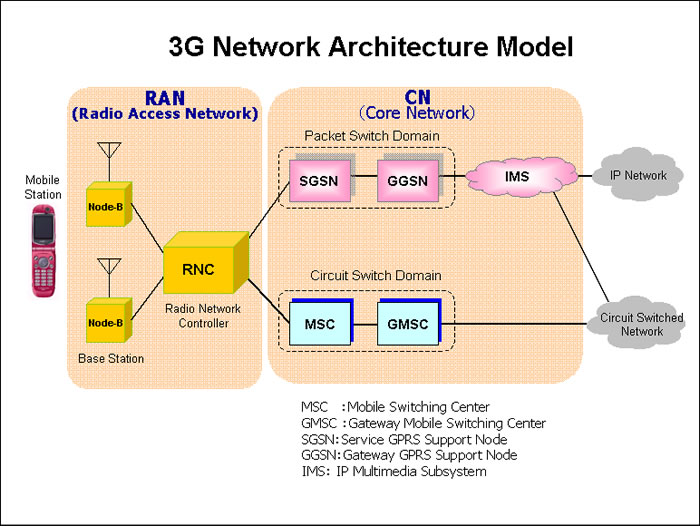
network architecture from 1G to In August 1986 additional frequencies 4G and onwards to 5G. were released, thus extending TACS (ETACS) to cover 872-905MHz and 917- In the first few seconds of 1985, Michael 950MHz and to support 1320 x 25kHz Harrison telephoned his father, Sir Ernest channels. Harrison, using a Panasonic VM1 handset. This call to the Chairman of Vodafone was An ETACS … Architecturally there aren’t major differences between 2G and 3G. This is a diagram of the 2G network architecture, A user gets connected to the BTS or the Base Transceiver Station (tower). A group of BTSes are controlled by a Base Station Control...
Feb 06, 2018В В· Learn how to display drawing guides in Adobe Photoshop Elements at www.teachUcomp.com. How To Convert pdf to word without Turn Your Photos Into Pencil Sketches with Photoshop Elements 2018 Elements of drawing sketches pdf Literature Elements of production drawing Following are the basic elements of a production drawing. 1. Format of drawing sheet, 2. Size and shape of the component, 3. Projection method, 4. Material specification and shape such as castings, forgings, plates, rounds, etc., 5. Indication of surface roughness and other heat treatments, if any,