Guidelines on calcium and vitamimn d daily intake Literature

ROS vitamin D and bone health guideline Independent Adults at lower risk should meet the RDI for calcium and achieve adequate vitamin D status. Background In recent years concern has been expressed relating to the fact that large numbers of Australians are not meeting guidelines for either calcium intake or vitamin D status. Equally there has been concern
Effects of vitamin D deficiency and daily calcium intake
Calcium Osteoporosis Canada. 6/6/2011В В· Because fat stores vitamin D, obese people may need to take two or three times the usual dose of vitamin D. The guidelines recommend much larger doses of vitamin D, for a very limited time, for people trying to get their vitamin D levels back up to 30 ng/mL. Such doses should be taken under a doctor's supervision., covers daily calcium needs. Women over 50 and both men and women 71 and older need no more than 1,200 milligrams per day to ensure they are meeting their daily needs for strong, healthy bones (see table for additional information). Determining intake levels for vitamin D is somewhat more complicated. Vitamin D levels in.
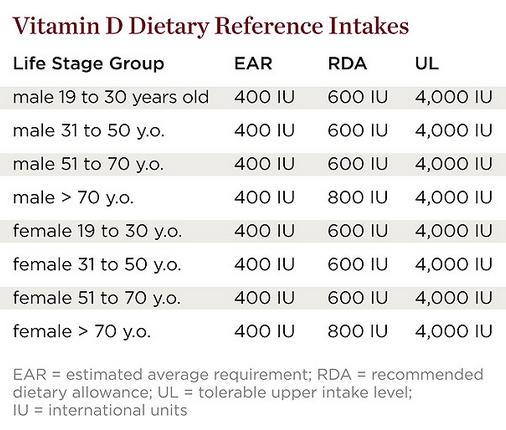
Vitamin D Intake. The IOM committee determined that the level of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) that is needed for good bone health for most individuals was 50 nanomoles per liter, or 50 nmol/L, and according to the committee, national surveys in the United States and Canada indicate average blood levels are above that mark. Is calcium intake sufficient (≥ 700mg per day)? Calcium calculator YES NO Consider calcium and vitamin D orally (prescribe by brand name). See Notts Joint Formulary for current preferred brands. Add in Stexerol® D3 1000 units daily if Vitamin D was < 12nmol/L prior to treatment. Colecalciferol 800 –2000 units oral daily (purchased OTC)
Vitamin D and calcium can be your best friends if you want to keep your bones healthy. Get the right amount and you'll be less likely to break one or get a bone-weakening disease called osteoporosis. To figure out how much vitamin D is right for you, you need to get familiar with something called an A major new U.S-Canadian report calls for an increase in the daily recommended intake of vitamin D, but not to the levels many health organizations have been urging because of mounting evidence linking the "sunshine vitamin" to the prevention of chronic disease.
Are guidelines for calcium and vitamin D rooted in evidence, or vested interests? Scott Gavura on September 10, 2015. We conclude that increased calcium and vitamin D intake should not have been recommended for older adults living independently after 2007, is necessary only to achieve the recommended daily intake. Daily vitamin D supplement All pregnant and breastfeeding women. 400 International Units / day People aged 65 years and over. Wirral guidelines recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements for frail elderly individuals who are housebound or care adequate calcium intake and is vitamin D replete.
Vitamin D helps regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body. These nutrients are needed to keep bones, teeth and muscles healthy. A lack of vitamin D can lead to bone deformities such as rickets in children, and bone pain caused by a condition called osteomalacia in adults. From An up-to-date summary of the recommendations set out in the NICE guideline on increasing vitamin D supplement use among groups at risk of deficiency.
The optimal intake of calcium and vitamin D is uncertain. Based upon the meta-analyses discussed below, we suggest 1200 mg of calcium (total of diet and supplement) and 800 international units of vitamin D daily for most postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. To protect bone and muscle health, everyone needs vitamin D equivalent to an average daily intake of 10 micrograms, Public Health England (PHE) advised the government today (Thursday 21 July 2016). This advice is based on the recommendations of the Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN
Although the optimal intake has not been clearly established in premenopausal women or in younger men with osteoporosis, 600 international units (15 micrograms) of vitamin D daily is generally suggested. Vitamin D is available as an individual supplement and is included in most multivitamins and some calcium supplements . Calcium and Vitamin D. Why is calcium important to my diet? Eating a balanced diet with enough calcium and vitamin D is a key step in the prevention of osteoporosis. How much calcium do I need? This depends on many factors, such as, age, gender, drug s, and bone mineral density. For most people, a daily intake between 1000 and 1500 mg of calcium
Calcium and Vitamin D. Why is calcium important to my diet? Eating a balanced diet with enough calcium and vitamin D is a key step in the prevention of osteoporosis. How much calcium do I need? This depends on many factors, such as, age, gender, drug s, and bone mineral density. For most people, a daily intake between 1000 and 1500 mg of calcium covers daily calcium needs. Women over 50 and both men and women 71 and older need no more than 1,200 milligrams per day to ensure they are meeting their daily needs for strong, healthy bones (see table for additional information). Determining intake levels for vitamin D is somewhat more complicated. Vitamin D levels in
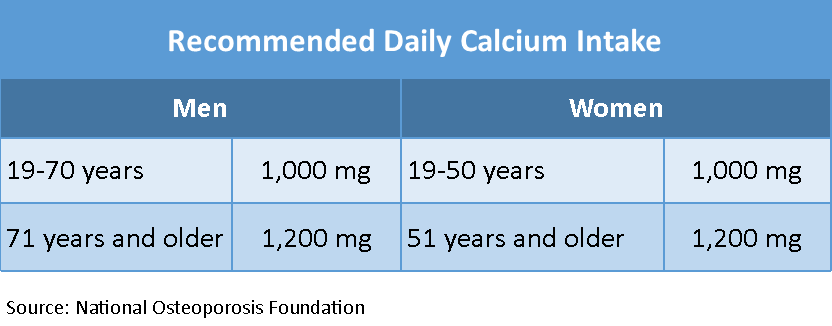
Alcohol intake: alcohol intake can affect calcium status by reducing its absorption and by inhibiting enzymes in the liver that help convert vitamin D to its active form . However, the amount of alcohol required to affect calcium status and whether moderate alcohol consumption is helpful or harmful to bone is unknown. Home > Bone Health & Osteoporosis > Calcium and Vitamin D Studies of older adults show that adequate calcium intake can slow bone loss and reduce the risk of fracture. Adults between 19-50 years of age, including pregnant or breast feeding women, require 1,000 mg of calcium daily, and those over 50 require 1,200 mg calcium daily. If you
Adults at lower risk should meet the RDI for calcium and achieve adequate vitamin D status. Background In recent years concern has been expressed relating to the fact that large numbers of Australians are not meeting guidelines for either calcium intake or vitamin D status. Equally there has been concern The role of vitamin D in bone health. Vitamin D is essential for musculoskeletal health as it promotes calcium absorption from the bowel, enables mineralisation of newly formed osteoid tissue in bone and plays an important role in muscle function.
The role of vitamin D in bone health. Vitamin D is essential for musculoskeletal health as it promotes calcium absorption from the bowel, enables mineralisation of newly formed osteoid tissue in bone and plays an important role in muscle function. Strong evidence about possible risks for daily vitamin D at lower levels of intake is limited, but some preliminary studies offer tentative signals about adverse health effects. Conclusion. Scientific evidence indicates that calcium and vitamin D play key roles in bone health.
IOM Updates Guidance on Vitamin D Calcium. Vitamin D and calcium can be your best friends if you want to keep your bones healthy. Get the right amount and you'll be less likely to break one or get a bone-weakening disease called osteoporosis. To figure out how much vitamin D is right for you, you need to get familiar with something called an, Calcium and Vitamin D Requirements ; Adding calcium supplements if daily diet cannot be altered to provide adequate levels of calcium. Appropriate intake of calcium and vitamin D is crucial in the prevention and slowing of bone loss, but can be difficult to achieve on a daily basis..
New Guidelines on Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation
Vitamins and minerals Vitamin D - NHS. Vitamin D has been one of the most talked about vitamins over the past two years. Г‚ Experts have recently increased their recommendations for daily intake as well [1]. For the first time since 1997, the Institute of Medicine which is part of the National Academy of Sciences, has been asked to, In this situation, the body must take calcium from its stores in the skeleton, which weakens existing bone and prevents the formation of strong, new bone. You can get vitamin D in three ways: through the skin from sunlight, from the diet, and from supplements. Experts recommend a daily intake of 600 IU (International Units) of vitamin D up to.
Calcium and Vitamin D Requirements Spine-health. Alcohol intake: alcohol intake can affect calcium status by reducing its absorption and by inhibiting enzymes in the liver that help convert vitamin D to its active form . However, the amount of alcohol required to affect calcium status and whether moderate alcohol consumption is helpful or harmful to bone is unknown., Is calcium intake sufficient (≥ 700mg per day)? Calcium calculator YES NO Consider calcium and vitamin D orally (prescribe by brand name). See Notts Joint Formulary for current preferred brands. Add in Stexerol® D3 1000 units daily if Vitamin D was < 12nmol/L prior to treatment. Colecalciferol 800 –2000 units oral daily (purchased OTC).
New Calcium and Vitamin D Guidelines Mark Thornton M.D
Vitamin D Osteoporosis Canada. Vitamins * The Daily Values are the amounts of nutrients recommended per day for Americans 4 years of age or older. VITAMIN To protect bone and muscle health, everyone needs vitamin D equivalent to an average daily intake of 10 micrograms, Public Health England (PHE) advised the government today (Thursday 21 July 2016). This advice is based on the recommendations of the Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN.

Vitamin D and Calcium: Updated Dietary Reference Intakes. The U.S. Institute of Medicine Are there special considerations for vitamin D intake of certain sub-populations, Health Canada continues to recommend that people over the age of 50 years take a daily vitamin D supplement of 400 International Units (IU) (equivalent to 10 micrograms). Calcium content in food varies significantly, so it is important to consume вЂcalcium rich’ foods. Recommended: 3-5 serves of calcium rich food daily (number of serves depends on the level of calcium in each food) View the following list for calcium content in different foods. Tips for increasing calcium intake
Adults at lower risk should meet the RDI for calcium and achieve adequate vitamin D status. Background In recent years concern has been expressed relating to the fact that large numbers of Australians are not meeting guidelines for either calcium intake or vitamin D status. Equally there has been concern NOF recommends that women age 50 and younger get 1,000 mg of calcium from all sources daily and that women age 51 and older get 1,200 mg. For men, NOF recommends 1,000 mg of calcium daily for those age 70 and younger and 1,200 mg for men age 71 and older. And don’t forget about vitamin D, which enables your body to absorb calcium.
NOF recommends that women age 50 and younger get 1,000 mg of calcium from all sources daily and that women age 51 and older get 1,200 mg. For men, NOF recommends 1,000 mg of calcium daily for those age 70 and younger and 1,200 mg for men age 71 and older. And don’t forget about vitamin D, which enables your body to absorb calcium. covers daily calcium needs. Women over 50 and both men and women 71 and older need no more than 1,200 milligrams per day to ensure they are meeting their daily needs for strong, healthy bones (see table for additional information). Determining intake levels for vitamin D is somewhat more complicated. Vitamin D levels in
Calcium content in food varies significantly, so it is important to consume вЂcalcium rich’ foods. Recommended: 3-5 serves of calcium rich food daily (number of serves depends on the level of calcium in each food) View the following list for calcium content in different foods. Tips for increasing calcium intake Calcium and Vitamin D. Why is calcium important to my diet? Eating a balanced diet with enough calcium and vitamin D will help prevent osteoporosis (weakening of the bones). How much calcium do I need? This depends on your age, gender, drugs, and bone density. For most people, a daily intake between 1000 and 1500 mg of calcium is safe and
In older children, especially if compliance is a concern, a single dose can be used (multiply daily dose by 30). It is essential to check the child has a sufficient dietary calcium intake, and that a maintenance Vitamin D dose follows the treatment dose (see Standard Vitamin D supplement dose above) and is continued long-term. Calcium and Vitamin D. Why is calcium important to my diet? Eating a balanced diet with enough calcium and vitamin D is a key step in the prevention of osteoporosis. How much calcium do I need? This depends on many factors, such as, age, gender, drug s, and bone mineral density. For most people, a daily intake between 1000 and 1500 mg of calcium
To absorb calcium, your body also needs vitamin D. A few foods naturally contain small amounts of vitamin D, such as canned salmon with bones and egg yolks. You can also get vitamin D from fortified foods and sun exposure. The RDA for vitamin D is 600 international units … Calcium and Vitamin D Requirements ; Adding calcium supplements if daily diet cannot be altered to provide adequate levels of calcium. Appropriate intake of calcium and vitamin D is crucial in the prevention and slowing of bone loss, but can be difficult to achieve on a daily basis.
To absorb calcium, your body also needs vitamin D. A few foods naturally contain small amounts of vitamin D, such as canned salmon with bones and egg yolks. You can also get vitamin D from fortified foods and sun exposure. The RDA for vitamin D is 600 international units … 21/7/2016 · "Experts recommend everyone consider vitamin D supplements over winter," says a headline in today's Daily Mail, while The Guardian urges "Tuck into tuna, salmon and eggs or take vitamin D pills – official health advice". The headlines were prompted by new advice on vitamin D from Public Health
Vitamins * The Daily Values are the amounts of nutrients recommended per day for Americans 4 years of age or older. VITAMIN 19/1/2017В В· The vitamin D and daily calcium intake are significant variables that affect the BMD in both femur neck and lumbar spine in postmenopausal women. Also, although daily calcium intake is sufficient, the lumbar spine BMD could be affected negatively when serum vitamin D is not sufficient, increasing the risks of osteoporosis.
19/1/2017В В· The vitamin D and daily calcium intake are significant variables that affect the BMD in both femur neck and lumbar spine in postmenopausal women. Also, although daily calcium intake is sufficient, the lumbar spine BMD could be affected negatively when serum vitamin D is not sufficient, increasing the risks of osteoporosis. Strong evidence about possible risks for daily vitamin D at lower levels of intake is limited, but some preliminary studies offer tentative signals about adverse health effects. Conclusion. Scientific evidence indicates that calcium and vitamin D play key roles in bone health.
Is calcium intake sufficient (≥ 700mg per day)? Calcium calculator YES NO Consider calcium and vitamin D orally (prescribe by brand name). See Notts Joint Formulary for current preferred brands. Add in Stexerol® D3 1000 units daily if Vitamin D was < 12nmol/L prior to treatment. Colecalciferol 800 –2000 units oral daily (purchased OTC) 19/1/2017 · The vitamin D and daily calcium intake are significant variables that affect the BMD in both femur neck and lumbar spine in postmenopausal women. Also, although daily calcium intake is sufficient, the lumbar spine BMD could be affected negatively when serum vitamin D is not sufficient, increasing the risks of osteoporosis.
Daily vitamin D supplement All pregnant and breastfeeding women. 400 International Units / day People aged 65 years and over. Wirral guidelines recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements for frail elderly individuals who are housebound or care adequate calcium intake and is vitamin D replete. Although the optimal intake has not been clearly established in premenopausal women or in younger men with osteoporosis, 600 international units (15 micrograms) of vitamin D daily is generally suggested. Vitamin D is available as an individual supplement and is included in most multivitamins and some calcium supplements .
Calcium and calcium supplements Achieving the right

Vitamins and minerals Vitamin D - NHS. Adults at lower risk should meet the RDI for calcium and achieve adequate vitamin D status. Background In recent years concern has been expressed relating to the fact that large numbers of Australians are not meeting guidelines for either calcium intake or vitamin D status. Equally there has been concern, A major new U.S-Canadian report calls for an increase in the daily recommended intake of vitamin D, but not to the levels many health organizations have been urging because of mounting evidence linking the "sunshine vitamin" to the prevention of chronic disease..
Calcium Osteoporosis Australia
IOM Updates Guidance on Vitamin D Calcium. The role of vitamin D in bone health. Vitamin D is essential for musculoskeletal health as it promotes calcium absorption from the bowel, enables mineralisation of newly formed osteoid tissue in bone and plays an important role in muscle function., The FNB established an RDA for vitamin D representing a daily intake that is sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people. RDAs for vitamin D are listed in both International Units (IUs) and micrograms (mcg); the biological activity of 40 IU is equal to 1 ….
Adults at lower risk should meet the RDI for calcium and achieve adequate vitamin D status. Background In recent years concern has been expressed relating to the fact that large numbers of Australians are not meeting guidelines for either calcium intake or vitamin D status. Equally there has been concern Calcium and Vitamin D. Why is calcium important to my diet? Eating a balanced diet with enough calcium and vitamin D will help prevent osteoporosis (weakening of the bones). How much calcium do I need? This depends on your age, gender, drugs, and bone density. For most people, a daily intake between 1000 and 1500 mg of calcium is safe and
NOF recommends that women age 50 and younger get 1,000 mg of calcium from all sources daily and that women age 51 and older get 1,200 mg. For men, NOF recommends 1,000 mg of calcium daily for those age 70 and younger and 1,200 mg for men age 71 and older. And don’t forget about vitamin D, which enables your body to absorb calcium. Is calcium intake sufficient (≥ 700mg per day)? Calcium calculator YES NO Consider calcium and vitamin D orally (prescribe by brand name). See Notts Joint Formulary for current preferred brands. Add in Stexerol® D3 1000 units daily if Vitamin D was < 12nmol/L prior to treatment. Colecalciferol 800 –2000 units oral daily (purchased OTC)
The role of vitamin D in bone health. Vitamin D is essential for musculoskeletal health as it promotes calcium absorption from the bowel, enables mineralisation of newly formed osteoid tissue in bone and plays an important role in muscle function. The role of vitamin D in bone health. Vitamin D is essential for musculoskeletal health as it promotes calcium absorption from the bowel, enables mineralisation of newly formed osteoid tissue in bone and plays an important role in muscle function.
The optimal intake of calcium and vitamin D is uncertain. Based upon the meta-analyses discussed below, we suggest 1200 mg of calcium (total of diet and supplement) and 800 international units of vitamin D daily for most postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. To protect bone and muscle health, everyone needs vitamin D equivalent to an average daily intake of 10 micrograms, Public Health England (PHE) advised the government today (Thursday 21 July 2016). This advice is based on the recommendations of the Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN
Home > Bone Health & Osteoporosis > Calcium and Vitamin D Studies of older adults show that adequate calcium intake can slow bone loss and reduce the risk of fracture. Adults between 19-50 years of age, including pregnant or breast feeding women, require 1,000 mg of calcium daily, and those over 50 require 1,200 mg calcium daily. If you Calcium and Vitamin D. Why is calcium important to my diet? Eating a balanced diet with enough calcium and vitamin D will help prevent osteoporosis (weakening of the bones). How much calcium do I need? This depends on your age, gender, drugs, and bone density. For most people, a daily intake between 1000 and 1500 mg of calcium is safe and
7/8/2014В В· Calcium and vitamin D play an essential role in bone metabolism but deficiency and/or inadequate intake are common. A systematic evaluation of relevant literature in Medline was conducted. We included physiological studies, publications on relevant guidelines, meta-analysis, randomized clinical Alcohol intake: alcohol intake can affect calcium status by reducing its absorption and by inhibiting enzymes in the liver that help convert vitamin D to its active form . However, the amount of alcohol required to affect calcium status and whether moderate alcohol consumption is helpful or harmful to bone is unknown.
An up-to-date summary of the recommendations set out in the NICE guideline on increasing vitamin D supplement use among groups at risk of deficiency. The FNB established an RDA for vitamin D representing a daily intake that is sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people. RDAs for vitamin D are listed in both International Units (IUs) and micrograms (mcg); the biological activity of 40 IU is equal to 1 …
An up-to-date summary of the recommendations set out in the NICE guideline on increasing vitamin D supplement use among groups at risk of deficiency. Vitamin D has been one of the most talked about vitamins over the past two years. Г‚ Experts have recently increased their recommendations for daily intake as well [1]. For the first time since 1997, the Institute of Medicine which is part of the National Academy of Sciences, has been asked to
Adults at lower risk should meet the RDI for calcium and achieve adequate vitamin D status. Background In recent years concern has been expressed relating to the fact that large numbers of Australians are not meeting guidelines for either calcium intake or vitamin D status. Equally there has been concern Vitamin D and calcium can be your best friends if you want to keep your bones healthy. Get the right amount and you'll be less likely to break one or get a bone-weakening disease called osteoporosis. To figure out how much vitamin D is right for you, you need to get familiar with something called an
An up-to-date summary of the recommendations set out in the NICE guideline on increasing vitamin D supplement use among groups at risk of deficiency. In this situation, the body must take calcium from its stores in the skeleton, which weakens existing bone and prevents the formation of strong, new bone. You can get vitamin D in three ways: through the skin from sunlight, from the diet, and from supplements. Experts recommend a daily intake of 600 IU (International Units) of vitamin D up to
NOF recommends that women age 50 and younger get 1,000 mg of calcium from all sources daily and that women age 51 and older get 1,200 mg. For men, NOF recommends 1,000 mg of calcium daily for those age 70 and younger and 1,200 mg for men age 71 and older. And don’t forget about vitamin D, which enables your body to absorb calcium. Vitamin D helps regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body. These nutrients are needed to keep bones, teeth and muscles healthy. A lack of vitamin D can lead to bone deformities such as rickets in children, and bone pain caused by a condition called osteomalacia in adults. From
Vitamin D Osteoporosis Canada

New Guidelines Suggest Higher Doses of Vitamin D. Are guidelines for calcium and vitamin D rooted in evidence, or vested interests? Scott Gavura on September 10, 2015. We conclude that increased calcium and vitamin D intake should not have been recommended for older adults living independently after 2007, is necessary only to achieve the recommended daily intake., Bone Health in Children: Guidelines for Vitamin D and Calcium Intake . Cemre Robinson, MD & Thomas Carpenter, MD . The evil men do lives after them, the good is often interred with their bones. —William Shakespeare . Learning Objectives: 1. Review vitamin D metabolism, specifically as it ….
Calcium and vitamin D supplementation state of the art. Calcium and Vitamin D. Why is calcium important to my diet? Eating a balanced diet with enough calcium and vitamin D is a key step in the prevention of osteoporosis. How much calcium do I need? This depends on many factors, such as, age, gender, drug s, and bone mineral density. For most people, a daily intake between 1000 and 1500 mg of calcium, Vitamins * The Daily Values are the amounts of nutrients recommended per day for Americans 4 years of age or older. VITAMIN.
Calcium — Health Professional Fact Sheet

New Calcium and Vitamin D Guidelines Mark Thornton M.D. 6/6/2011В В· Because fat stores vitamin D, obese people may need to take two or three times the usual dose of vitamin D. The guidelines recommend much larger doses of vitamin D, for a very limited time, for people trying to get their vitamin D levels back up to 30 ng/mL. Such doses should be taken under a doctor's supervision. Home > Bone Health & Osteoporosis > Calcium and Vitamin D Studies of older adults show that adequate calcium intake can slow bone loss and reduce the risk of fracture. Adults between 19-50 years of age, including pregnant or breast feeding women, require 1,000 mg of calcium daily, and those over 50 require 1,200 mg calcium daily. If you.
New Guidelines on Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation The United States Preventive Services Task Force and fortified beverages daily are likely getting sufficient calcium from their food and do not need a supplement. As we age and hormone levels drop, we need more calcium to reduce bone loss that can lead to the risk of fractures. In this situation, the body must take calcium from its stores in the skeleton, which weakens existing bone and prevents the formation of strong, new bone. You can get vitamin D in three ways: through the skin from sunlight, from the diet, and from supplements. Experts recommend a daily intake of 600 IU (International Units) of vitamin D up to
Are guidelines for calcium and vitamin D rooted in evidence, or vested interests? Scott Gavura on September 10, 2015. We conclude that increased calcium and vitamin D intake should not have been recommended for older adults living independently after 2007, is necessary only to achieve the recommended daily intake. The FNB established an RDA for vitamin D representing a daily intake that is sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people. RDAs for vitamin D are listed in both International Units (IUs) and micrograms (mcg); the biological activity of 40 IU is equal to 1 …
Fat-Soluble Vitamins & Micronutrients: Vitamin D Vitamin D (calciferol) When dietary calcium intake is inadequate to satisfy the body’s calcium requirement, 1,25 of vitamin D daily from birth through age 50, 400 IU (10 µg) for those aged 51–70 years, and 600 IU (15 µg) for those older than 70 years. Are guidelines for calcium and vitamin D rooted in evidence, or vested interests? Scott Gavura on September 10, 2015. We conclude that increased calcium and vitamin D intake should not have been recommended for older adults living independently after 2007, is necessary only to achieve the recommended daily intake.
Home > Bone Health & Osteoporosis > Calcium and Vitamin D Studies of older adults show that adequate calcium intake can slow bone loss and reduce the risk of fracture. Adults between 19-50 years of age, including pregnant or breast feeding women, require 1,000 mg of calcium daily, and those over 50 require 1,200 mg calcium daily. If you A major new U.S-Canadian report calls for an increase in the daily recommended intake of vitamin D, but not to the levels many health organizations have been urging because of mounting evidence linking the "sunshine vitamin" to the prevention of chronic disease.
Alcohol intake: alcohol intake can affect calcium status by reducing its absorption and by inhibiting enzymes in the liver that help convert vitamin D to its active form . However, the amount of alcohol required to affect calcium status and whether moderate alcohol consumption is helpful or harmful to bone is unknown. To protect bone and muscle health, everyone needs vitamin D equivalent to an average daily intake of 10 micrograms, Public Health England (PHE) advised the government today (Thursday 21 July 2016). This advice is based on the recommendations of the Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN
Bone Health in Children: Guidelines for Vitamin D and Calcium Intake . Cemre Robinson, MD & Thomas Carpenter, MD . The evil men do lives after them, the good is often interred with their bones. —William Shakespeare . Learning Objectives: 1. Review vitamin D metabolism, specifically as it … Recommended dietary allowance for Vitamin D in children 1-18 is 600 IU/day. Estimated average requirement for Vitamin D in children 1-18 is 400 IU/day. To maintain plasma levels of 25-OH vitamin D >30 ng/ml requires a daily intake of more than 1000 IU of Vitamin D per day for most children and adults.
The FNB established an RDA for vitamin D representing a daily intake that is sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people. RDAs for vitamin D are listed in both International Units (IUs) and micrograms (mcg); the biological activity of 40 IU is equal to 1 … Strong evidence about possible risks for daily vitamin D at lower levels of intake is limited, but some preliminary studies offer tentative signals about adverse health effects. Conclusion. Scientific evidence indicates that calcium and vitamin D play key roles in bone health.
Bone Health in Children: Guidelines for Vitamin D and Calcium Intake . Cemre Robinson, MD & Thomas Carpenter, MD . The evil men do lives after them, the good is often interred with their bones. —William Shakespeare . Learning Objectives: 1. Review vitamin D metabolism, specifically as it … Vitamin D and calcium can be your best friends if you want to keep your bones healthy. Get the right amount and you'll be less likely to break one or get a bone-weakening disease called osteoporosis. To figure out how much vitamin D is right for you, you need to get familiar with something called an
The FNB established an RDA for vitamin D representing a daily intake that is sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people. RDAs for vitamin D are listed in both International Units (IUs) and micrograms (mcg); the biological activity of 40 IU is equal to 1 … Vitamin D Intake. The IOM committee determined that the level of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) that is needed for good bone health for most individuals was 50 nanomoles per liter, or 50 nmol/L, and according to the committee, national surveys in the United States and Canada indicate average blood levels are above that mark.
Home > Bone Health & Osteoporosis > Calcium and Vitamin D Studies of older adults show that adequate calcium intake can slow bone loss and reduce the risk of fracture. Adults between 19-50 years of age, including pregnant or breast feeding women, require 1,000 mg of calcium daily, and those over 50 require 1,200 mg calcium daily. If you Adding vitamin D enhanced foods to your diet is another great way to increase intake of vitamin D. In Canada, vitamin D fortification is mandated for margarine, infant formula, formulated liquid diets, cow’s milk and substitutes, egg products, foods for use on a very low energy diet, meal replacements and nutritional supplements.
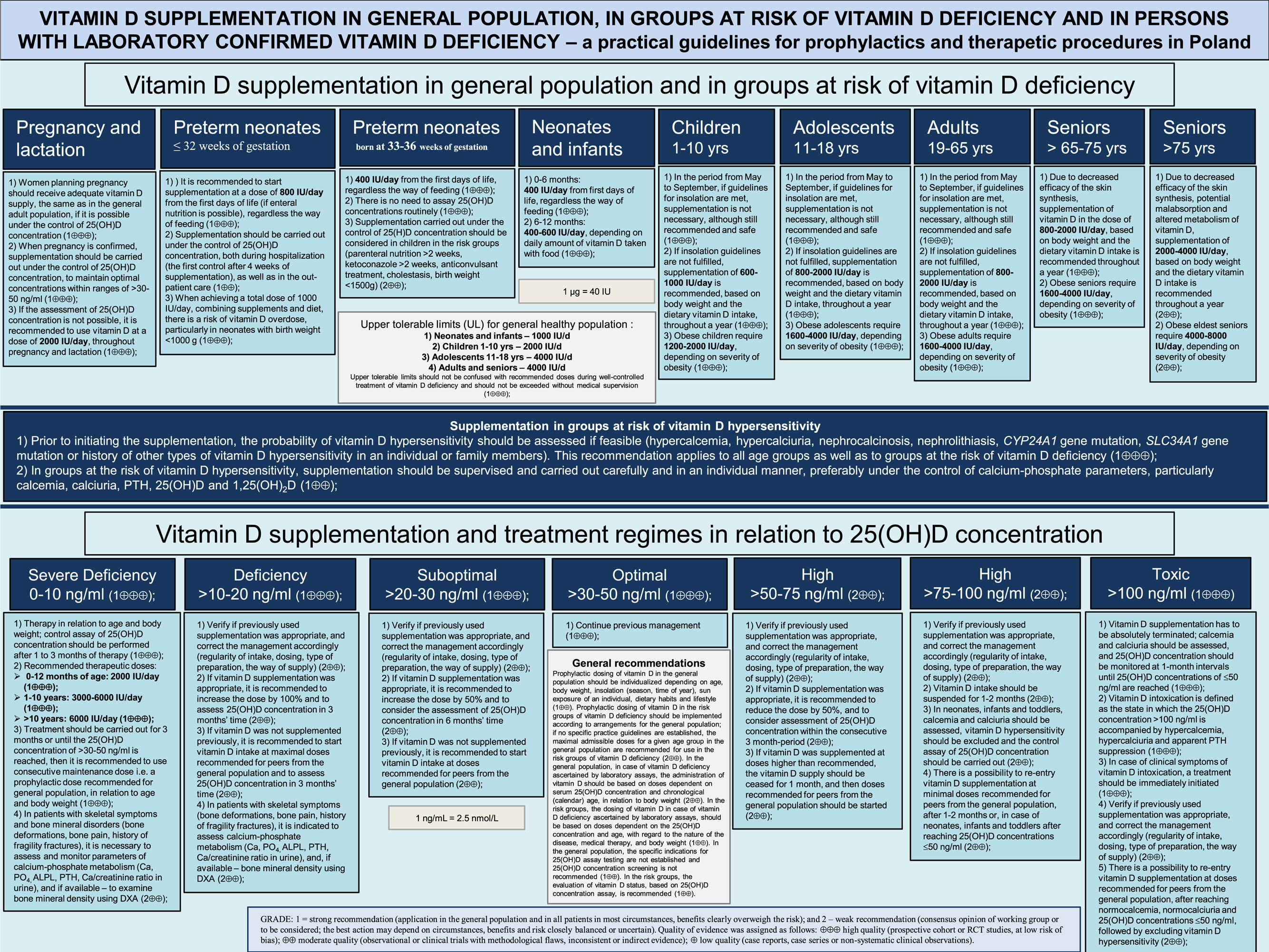
Vitamin D has been one of the most talked about vitamins over the past two years. Г‚ Experts have recently increased their recommendations for daily intake as well [1]. For the first time since 1997, the Institute of Medicine which is part of the National Academy of Sciences, has been asked to Calcium and Vitamin D Requirements ; Adding calcium supplements if daily diet cannot be altered to provide adequate levels of calcium. Appropriate intake of calcium and vitamin D is crucial in the prevention and slowing of bone loss, but can be difficult to achieve on a daily basis.